Begonias (Begonia, family Begoniaceae) are vibrant ornamental plants that transform homes, apartments, and gardens with their stunning diversity. With over 1,500 species and more than 1,000 cultivars, begonia cultivation offers endless possibilities for begonia gardening enthusiasts.
This begonia planting guide explores 25 captivating begonia varieties, categorized by growth habits and visual characteristics, and provides expert tips for how to grow begonias, begonia care, pest and disease management (begonia pest control), and more. Whether you’re a beginner or seasoned gardener, begonias will elevate your begonia gardening experience.
- Cane-Like or Garden Begonias
- Trailing Begonias
- Tuberous or Rhizomatous Begonias
- Foliage Begonias
- Manicata Begonia
- Heracleifolia Begonia
- Erythrophylla or Fista Begonia
- Large-Flowered Begonias
- Boliviensis Begonia
- Caudex or Dregei Begonia
- Begonia Care Tips
- Pest and Disease Management
- Gallery of Additional Varieties
- Conclusion: Transform Your Space with Begonias
Cane-Like or Garden Begonias
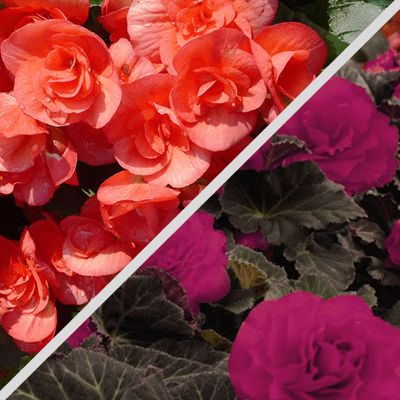

Cane-like begonias, also known as garden begonias (cane-like begonias), are prized for their ease of cultivation and prolific blooms, making them a favorite for how to grow begonias in pots or garden beds. These plants can flower year-round indoors, with heights ranging from 10 cm to 3 meters. Their small but abundant flowers create a dazzling display for begonia gardening.
Characteristics: Sturdy, cane-like stems with green or silvery leaves and clusters of pink, red, or white flowers. They thrive in bright, indirect light and require moderate begonia watering needs.
Popular Varieties:
- Fuchsioides (B. fuchsioides): Vibrant pink to deep red flowers, perfect for windowsills and begonia container gardening.
- Corallina (B. corallina): Delicate shades with silvery leaf speckles, ideal for garden beds.
Cultivation Tips: Use well-drained soil with pH 5.5–6.5 (begonia soil requirements). In Ukraine, plant outdoors in May after the last frost to ensure healthy growth. Water weekly, keeping soil moist but not waterlogged (begonia care).
Trailing Begonias
Trailing begonias (trailing begonias) create a cascading “floral waterfall,” ideal for hanging baskets and begonia container gardening. Their drooping stems reach 25–40 cm, with flowers up to 8–9 cm, blooming from June to October.
Characteristics: Flexible stems, lush green leaves, and vibrant flowers in pink, white, or orange. Tuberous types excel outdoors, while leafy varieties thrive indoors.
Popular Varieties:
- Alkor: Bright pink blooms for stunning displays.
- Illumination White: White flowers, perfect for balconies.
- Golden Balcony: Yellow-orange clusters, adding warmth to begonia gardening.
- Carmen: Deep pink flowers for dramatic effect.
Cultivation Tips: Provide bright, indirect light and water 1–2 times weekly (begonia watering needs). For tuberous varieties, store tubers at +10°C in dry conditions during winter dormancy to support begonia cultivation.


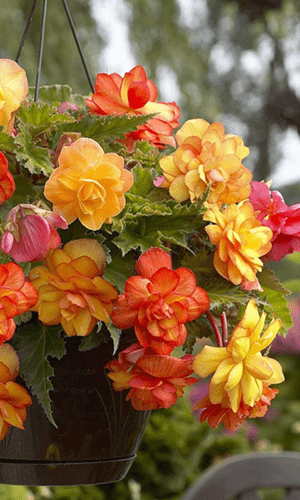

Tuberous or Rhizomatous Begonias
Tuberous begonias (tuberous begonias) are celebrated for their large, showy flowers and extended blooming period (March–October). Their tubers grow larger each year, simplifying how to grow begonias.
Characteristics: Wavy, fuzzy green leaves and flowers up to 20 cm, single or double. Fertilize biweekly with a balanced fertilizer (NPK 10-10-10, begonia fertilization) for optimal growth.
Popular Varieties:
- Kelblutrot: Striking red double flowers.
- Prima Donna: Pink flowers with ruffled petals.
- Picotee: White-pink blooms with colored edges.
- Marmorata: Marbled petal patterns for unique begonia varieties.
Cultivation Tips: Sow tubers indoors in February–March, transplant to gardens in May (Ukraine). Store tubers in a cool, dry place during winter to maintain begonia care standards.




Foliage Begonias
Foliage begonias (rex and foliage begonias) are grown for their striking leaves, which vary in shape (round, triangular) and color (burgundy, green, yellow). These low-maintenance plants are perfect for begonia cultivation indoors.
Characteristics: Leaves feature speckles, veins, or metallic sheen; flowers are small and less prominent. They require indirect light and careful watering.
Popular Varieties:
- Mallet: Leaves with white speckles, adding texture.
- Spotted (B. maculata): Silver-spotted leaves resembling angel wings.
- Carolineifolia (B. carolineifolia): Yellow-green leaves with bold veins, blooming in February.
- Metallica (B. metallica): Metallic sheen leaves, burgundy or green underside.
- Rex: Fringed leaves with vibrant patterns, a standout in begonia varieties.
Cultivation Tips: Water every 5–7 days, avoiding overwatering (begonia watering needs). Keep away from direct sunlight to prevent leaf burn (begonia care).





Manicata Begonia
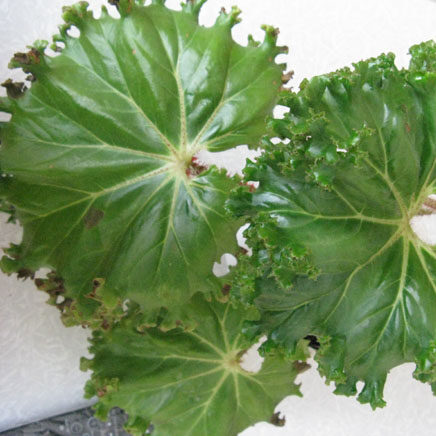

Manicata begonia (B. manicata) is named for its collar-like, ruffled leaves, adding elegance to begonia gardening.
Cultivation Tips: Provide indirect light and moderate watering. Protect from cold drafts to prevent begonia disease prevention issues.
Characteristics: Light green leaves up to 20 cm with ruffled edges, small clustered flowers. Blooms in winter (January–February). Grows up to 60 cm.
Heracleifolia Begonia
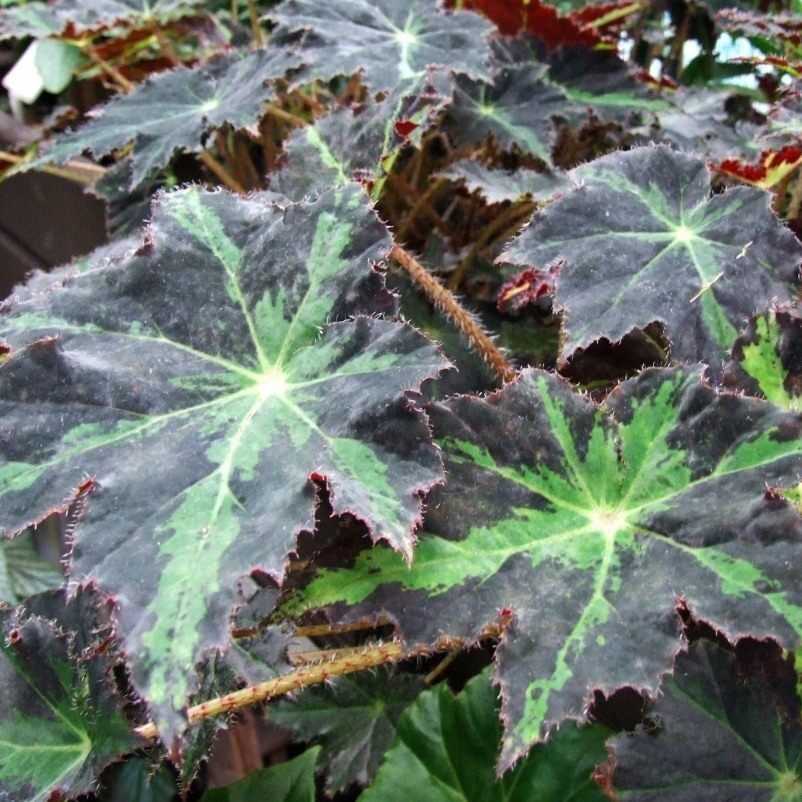

Heracleifolia begonia (B. heracleifolia) features large leaves (up to 30 cm) in green or reddish-brown hues with fuzzy surfaces, ideal for begonia cultivation.
- Characteristics: Leaves have dark or light spots, fuzzy stems, and small pink flowers.
- Cultivation Tips: Place in bright light, water every 5–7 days. High humidity promotes lush foliage (begonia soil requirements).
Erythrophylla or Fista Begonia
Erythrophylla begonia (B. erythrophylla ‘Fista’) boasts glossy green leaves with red undersides, making it a vibrant choice for begonia cultivation indoors.
Cultivation Tips: Water every 4–5 days, avoiding overwatering to prevent fungal issues (begonia disease prevention).
Characteristics: Compact, with delicate pink flowers. Requires frequent watering but is sensitive to repositioning.

Large-Flowered Begonias
Large-flowered begonias (tuberous hybrids) produce double flowers up to 20–30 cm outdoors and 15–20 cm indoors, perfect for vibrant begonia gardening.
Popular Varieties:
- Dark Red: Deep red blooms for bold displays.
- Diana Wynyard: White double flowers, elegant and timeless.
- Fimbriata: Ruffled petals for added texture.
- Double: Multicolored double blooms for variety.
Cultivation Tips: Fertilize biweekly with a balanced fertilizer (begonia fertilization). In Ukraine, plant in May for stunning summer blooms.




Boliviensis Begonia
Boliviensis begonia (B. boliviensis) features serrated, elongated leaves and bell-shaped flowers in pink, orange, or red, ideal for begonia container gardening.
Characteristics: Grows 30–50 cm, with varieties like Santa Cruz Sunset, Copacabana, and Bossa Nova.
Cultivation Tips: Plant in baskets, water moderately, and place in sunny spots for optimal begonia care.



Caudex or Dregei Begonia
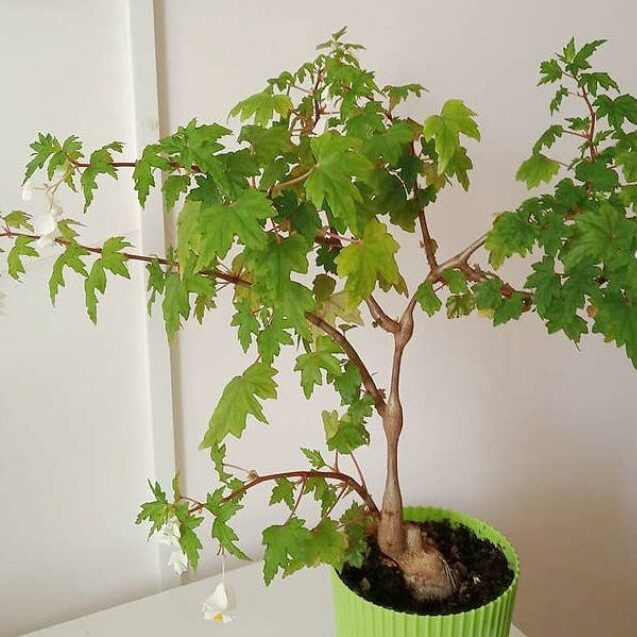

Caudex begonia (B. dregei) resembles succulents with a thickened stem base (caudex) that stores water, making it highly low-maintenance.
Cultivation Tips: Water every 7–10 days, keep in partial shade. Perfect for beginners in how to grow begonias.
Characteristics: Tolerates low light, can be shaped as a bonsai. Produces small white flowers.
Begonia Care Tips
To succeed in begonia cultivation, follow these essential begonia care guidelines:

- Soil: Use light, well-drained soil with pH 5.5–6.5 (begonia soil requirements). A mix of peat, perlite, and compost is ideal.
- Watering: Water 1–2 times weekly, ensuring no waterlogging (begonia watering needs). Tuberous varieties require no watering during winter dormancy.
- Lighting: Provide 12–14 hours of bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sun for foliage varieties to prevent leaf scorch.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer (NPK 10-10-10) biweekly during the growing season, reducing nitrogen during blooming (begonia fertilization).
- Pruning: Remove dead leaves and spent flowers (begonia pruning tips) to encourage growth and maintain plant health.
Pest and Disease Management
Begonias are susceptible to fungal diseases and pests, requiring diligent begonia pest control and begonia disease prevention.
- Powdery Mildew: White coating on leaves due to high humidity. Prevention: Ensure good air circulation through begonia crop rotation and avoid overwatering. Treatment: Spray with a soda-soap solution (0.5% baking soda, 40 g soap per 10 L water) or fungicides like Fundazol or Topaz.
- Aphids: Sucking insects leaving sticky residue. Control: Wash off with a strong water jet or apply Aktara for effective begonia pest control.
- Spider Mites: Cause leaf yellowing and spotting. Control: Treat with a soap solution or Aktofit, inspecting plants regularly.
Gallery of Additional Varieties




Discover these additional begonia varieties to inspire your begonia gardening:
- Nonstop: Tuberous begonia with vivid yellow or pink flowers, perfect for garden beds.
- Dragon Wing: Cane-like begonia with bold red blooms, ideal for begonia container gardening.
- Gryphon: Foliage begonia with large, silvery leaves for dramatic indoor displays.
Conclusion: Transform Your Space with Begonias
Begonias (Begonia) are a cornerstone of begonia gardening, offering an array of shapes, colors, and textures to suit any space. From the vibrant Fuchsioides to the cascading Illumination White, these begonia varieties bring elegance and charm to gardens, balconies, and homes. Whether you choose the low-maintenance Rex for its striking foliage or the showy Picotee for its large blooms, how to grow begonias is a rewarding journey.
Start your begonia cultivation today in pots, hanging baskets, or garden beds, following simple begonia care tips like proper soil, watering, and begonia pest control. Pair with begonia companion plants like ferns or hostas for a stunning display. For more expert advice, explore resources like rhs.org.uk or the American Begonia Society. Let begonias brighten your world with their timeless beauty!
If you have found a spelling error, please, notify us by selecting that text and pressing Ctrl+Enter.








